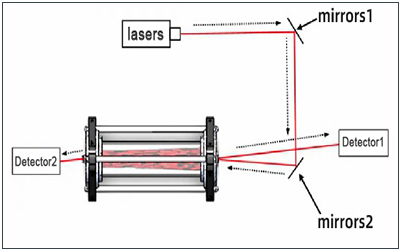
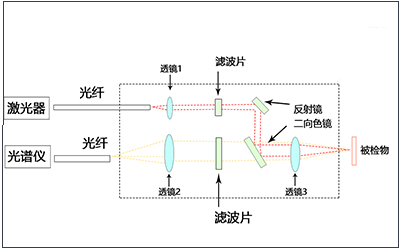
Optical components required for laser light sources
Windows
Calcium fluoride windows, barium fluoride windows, magnesium fluoride windows, silicon windows, germanium windows, zinc selenide windows, zinc sulfide windows, sapphire windows, fused silica windows, lithium fluoride windows, K9 glass windows
Lens
Planar convex lens, planar concave lens, biconvex lens, biconvex lens, meniscus lens
Filters
Germanium long wave pass filters, silicon long wave pass filters
prisms
Right-angle prisms
Mirrors
Galvanometers
1064nm galvanometers, 532nm galvanometers, 355nm galvanometers, 10.6 μ m galvanometers
Classification of laser light sources
Solid state laser light source
Using solid substances (such as crystals, glass, etc.) as working materials has the advantages of simple structure, small volume, and high output power.
Gas laser light source
Using gases (such as helium neon, carbon dioxide, etc.) as working materials, it has advantages such as good monochromaticity and good beam quality.
Liquid laser light source
Using liquids (such as organic dye solutions) as working materials has advantages such as tunability and high conversion efficiency.
Semiconductor laser source
Using semiconductor materials such as gallium arsenide and indium gallium arsenide as working materials has the advantages of small volume, low power consumption, and long lifespan.
The application of laser light sources
Laser cutting, laser welding, laser drilling, laser surgical knife, laser beauty instrument, laser spectral analysis, laser interferometry, laser weapons, laser radar, etc