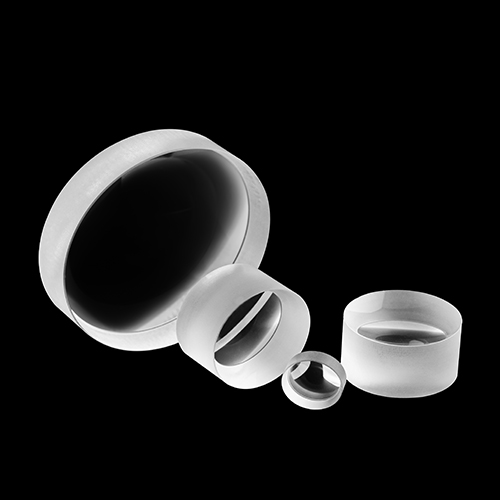
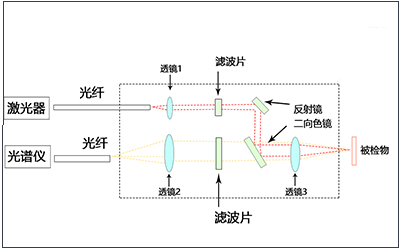
Optical components required for laser internal optical path
Windows
Calcium fluoride windows, barium fluoride windows, magnesium fluoride windows, silicon windows, germanium windows, zinc selenide windows, zinc sulfide windows, sapphire windows, fused silica windows, lithium fluoride windows, K9 glass windows
Lens
Planar convex lens, planar concave lens, biconvex lens, biconvex lens, meniscus lens
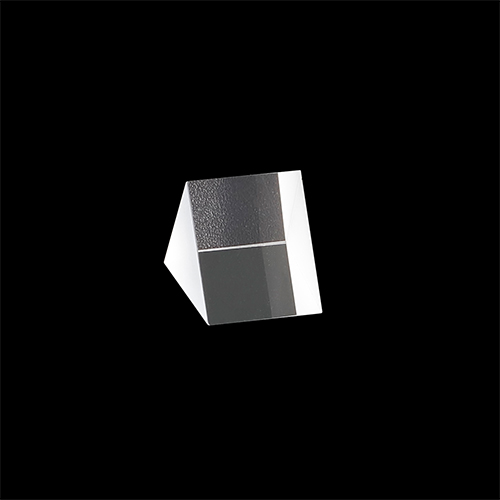
Prisms
Right-angle prisms
Galvanometers
1064nm galvanometers, 532nm galvanometers, 355nm galvanometers, 10.6 μ m galvanometers
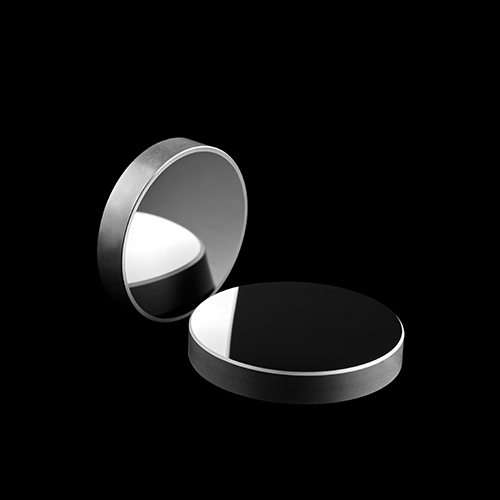
Reflector, output mirror, tail mirror
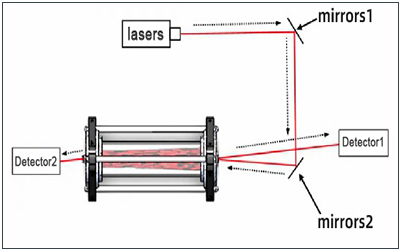
Classification of laser internal optical path
Linear internal optical path
The laser beam propagates in a straight line inside the laser and is focused and turned through components such as mirrors or lenses. Suitable for most lasers.
Folding internal optical path
In order to reduce the volume of the laser or meet special application requirements, the laser beam is reflected and folded multiple times inside the laser through components such as mirrors. It can make the laser more compact, but the design and adjustment are relatively complex.
Fiber optic internal optical path
Fiber laser uses fiber as the transmission medium for the laser beam, and couples the laser beam into the fiber through a fiber coupling system for transmission. Fiber optic internal optical path has advantages such as low transmission loss and good beam quality.
Application of laser internal optical path
Laser communication, laser ranging, laser velocimetry, laser processing, laser medicine, laser holography.