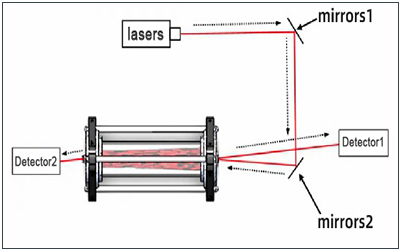
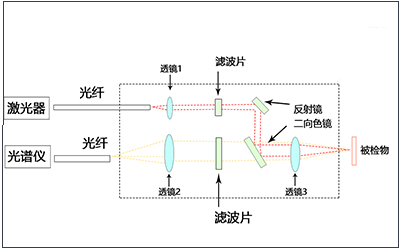
Optical components required for detection and sensing
Windows
Calcium Fluoride Windows, Barium Fluoride Windows, Magnesium Fluoride Windows, Silicon Windows, Germanium Windows, Zinc Selenide Windows, Zinc Sulfide Windows, Sapphire Windows,Fused Silica Windows, Lithium Fluoride Windows, K9 Glass Windows
Wedge Optical Windows
Calcium Fluoride Wedge Windows、Barium Fluoride Wedge Windows、Sapphire Wedge Windows
Filters
Germanium long wave pass filters, Silicon long wave pass filters
Planoconvex Lens
Calcium Fluoride Planoconvex Lenses、K9 Planoconvex Lens、Fused Silica Planoconvex Lens、Zinc Selenide Planoconvex Lens、Zinc Sulfide Planoconvex Lens、Germanium Planoconvex Lens、Silicon Planoconvex Lens、Lithium Fluoride Planoconvex Lens、Magnesium Fluoride Planoconvex Lens、Barium Fluoride Planoconvex Lens
Aspheric Planoconvex Lens
Sulfide Based Glass Aspherical Lens、Zinc Selenide Aspheric Lens、Zinc Sulfide Aspherical Lens、Germanium Aspherical Lens、Silicon Aspherical Lens
Classification of detection sensors
Gas sensing
A gas sensor is a converter that converts a certain gas volume fraction into a corresponding electrical signal. The detection head regulates the gas sample through gas sensors, including filtering out impurities and interfering gases, drying or refrigeration treatment, and other steps. The principle is based on the interaction between gas molecules and the measurement of electrical signals. Typically, gas sensors consist of two main components: sensor components and signal converters. Applied in consumer electronics, industrial safety, HVAC markets, etc.
Temperature sensing
A temperature sensor is the core part of a temperature measuring instrument, which can sense temperature and convert it into a usable output signal. The principle is to determine the temperature by measuring the change in heat of an object. Applied in industrial control, environmental monitoring, medical equipment, automobiles, household appliances, agriculture and other fields.
Flame detection
Flame detection is mainly based on detecting the special wavelengths of ultraviolet, infrared, and visible light emitted by flames, while also recognizing the flicker frequency of flame characteristics to detect flames. Flame detection is widely used in high-voltage areas, scenic spots, hazardous areas on construction sites, chemical stacking areas, safety production workshops, locations of centralized charging electric vehicle charging stations, indoor substations, new energy, petroleum and petrochemical, and other firefighting applications.
Non cooled detection
Non cooled detectors are devices that utilize the unique thermal effects of infrared radiation for operation. It does not require external refrigeration equipment to reduce the temperature of the detection components, and has advantages such as small size, light weight, low power consumption, and relatively low price. The principle is that when infrared radiation is irradiated on the sensitive components of the detector, the temperature of the sensitive components will change, resulting in a change in one of its physical parameters (such as resistance).